Checks
Checks — Options
The Checks — Options panel is where you control the settings for injecting checks into your application. You enable or disable check injection, define annotation processing, and select the runtime Java environment for the application.
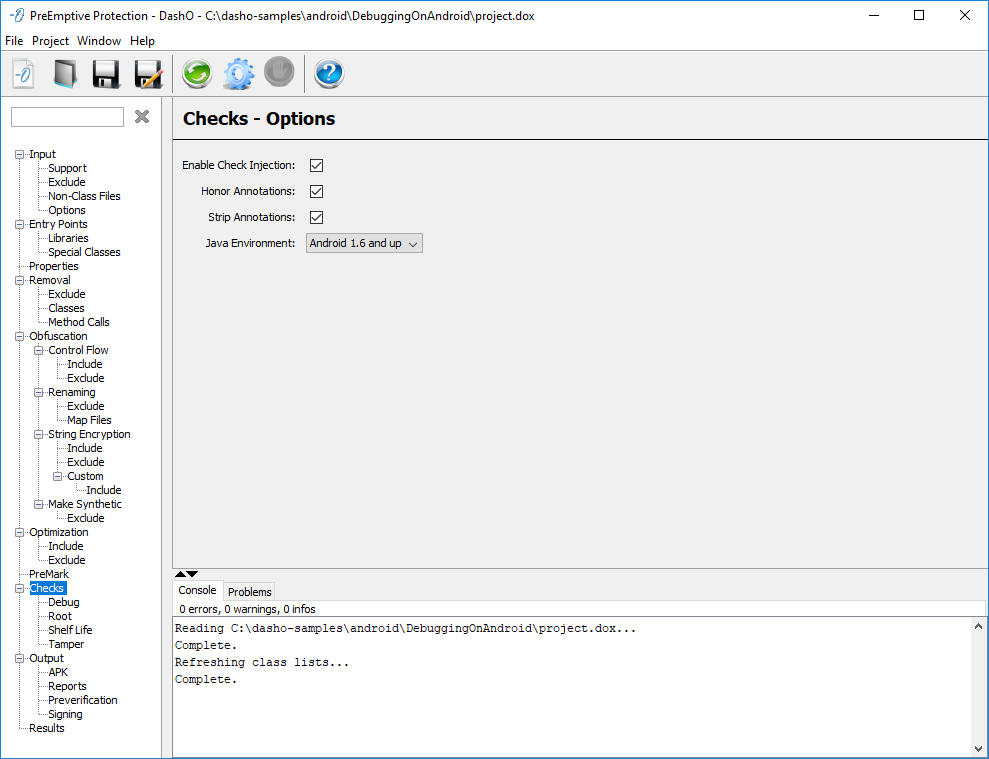
Enable Check Injection
Enables or disables the feature. Injection is used to add Tamper Checks, Debug Checks, Root Checks and Shelf Life expiration to the application.
Honor Annotations
Should PreEmptive Check annotation references in the code be honored or ignored? Annotations in the code are merged with check settings to determine the full list of checks.
Strip Annotations
Should PreEmptive Check annotation references be removed from the input classes?
Java Environment
This selects the runtime environment of your application and determines which Check implementations and Shelf Life implementation jar will be used.
Checks — Debug
The Checks — Debug panel is where you configure DebuggingChecks, DebuggingResponses, DebugEnabledChecks, and DebugEnabledResponses.
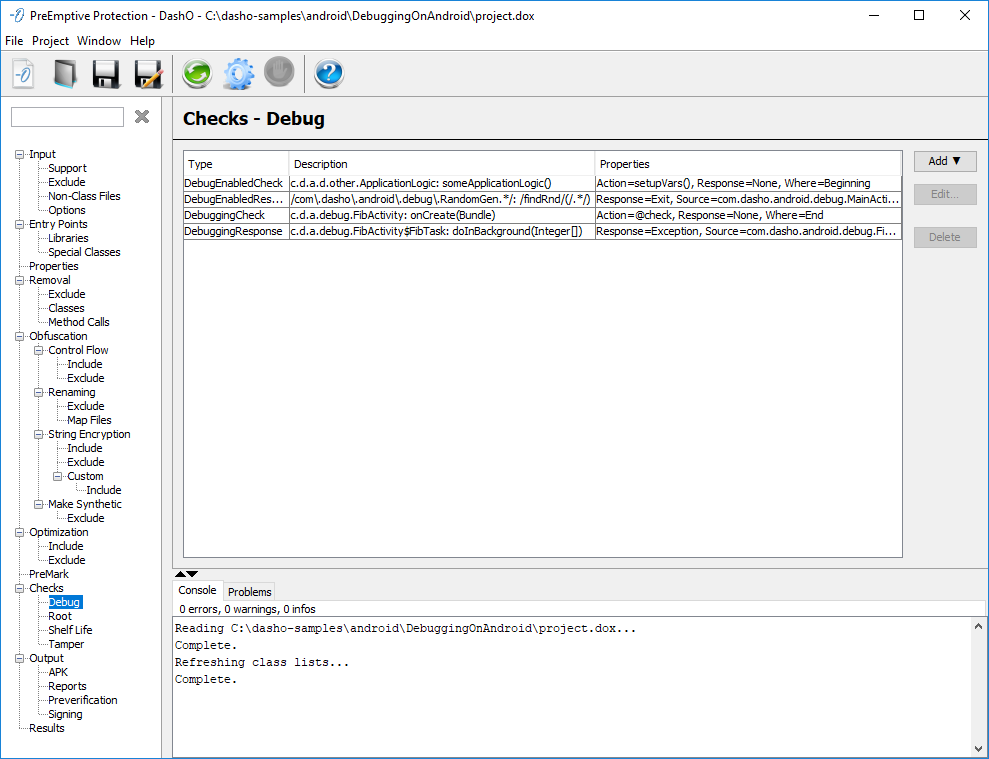
The Type column shows the type of Check or Response. The Description column describes the locations in the code, the methods and classes, where the Check or Response will be injected. The Properties column shows the settings for that particular Check or Response. The tooltips expand to show more details about the locations or properties.
Debugging Check
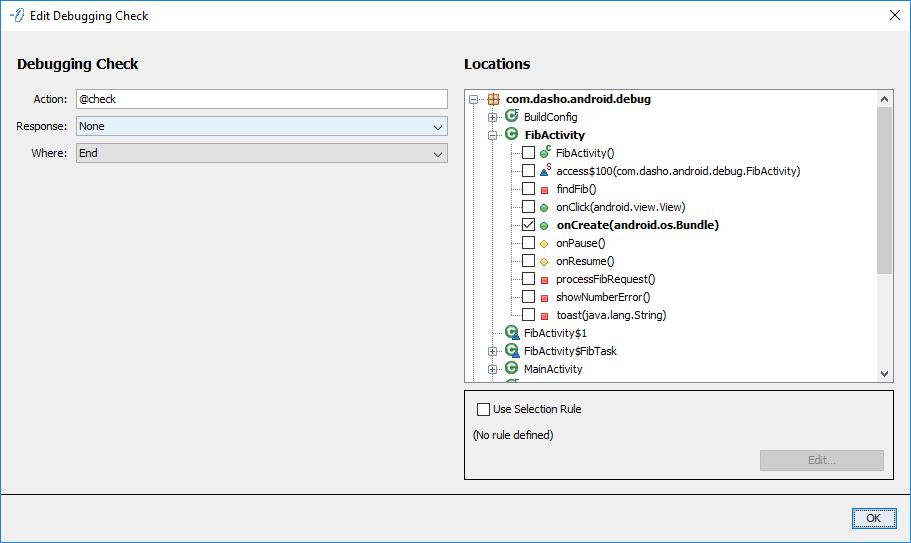
Configures a DebuggingCheck to be injected in the selected Locations. The Debugging Check uses the standard configuration.
Debugging Response
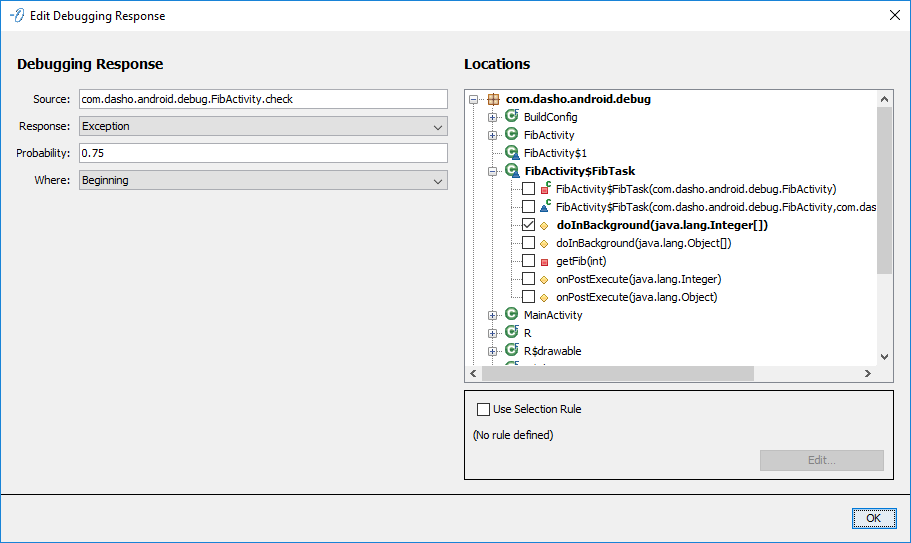
Configures a DebuggingResponse to be injected in the selected Locations. The Debugging Response uses the standard configuration.
Debug Enabled Check
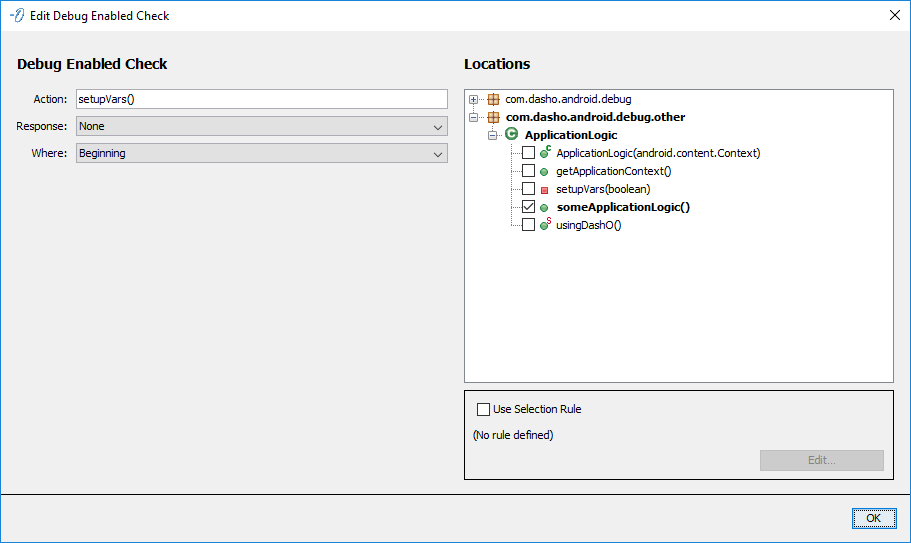
Configures a DebugEnabledCheck to be injected in the selected Locations. The Debug Enabled Check uses the standard configuration.
Debug Enabled Response
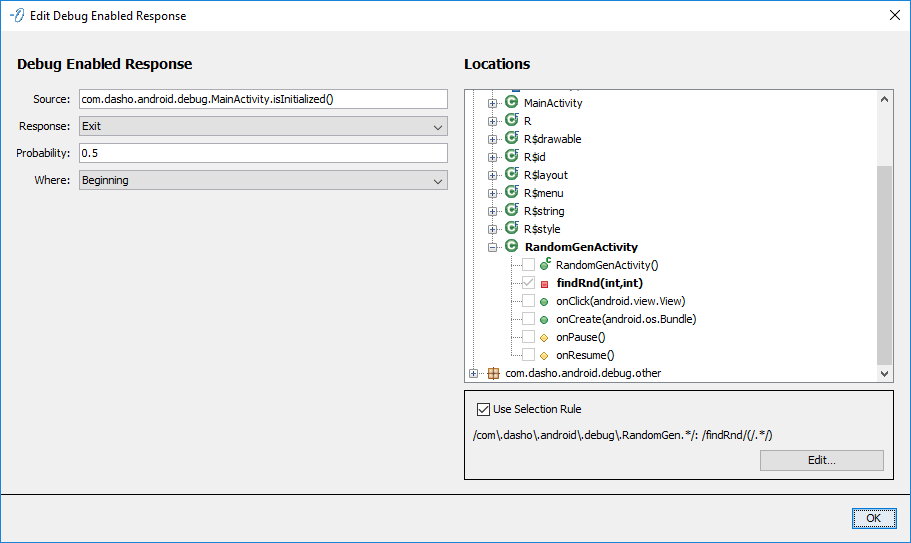
Configures a DebugEnabledResponse to be injected in the selected Locations. The Debug Enabled Response uses the standard configuration.
Checks — Root
The Checks — Root panel is where you configure RootChecks and RootResponses.

The Type column shows the type of Check or Response. The Description column describes the locations in the code, the methods and classes, where the Check or Response will be injected. The Properties column shows the settings for that particular Check or Response. The tooltips expand to show more details about the locations or properties.
Root Check

Configures a RootCheck to be injected in the selected Locations. The Root Check uses the standard configuration.
Root Response
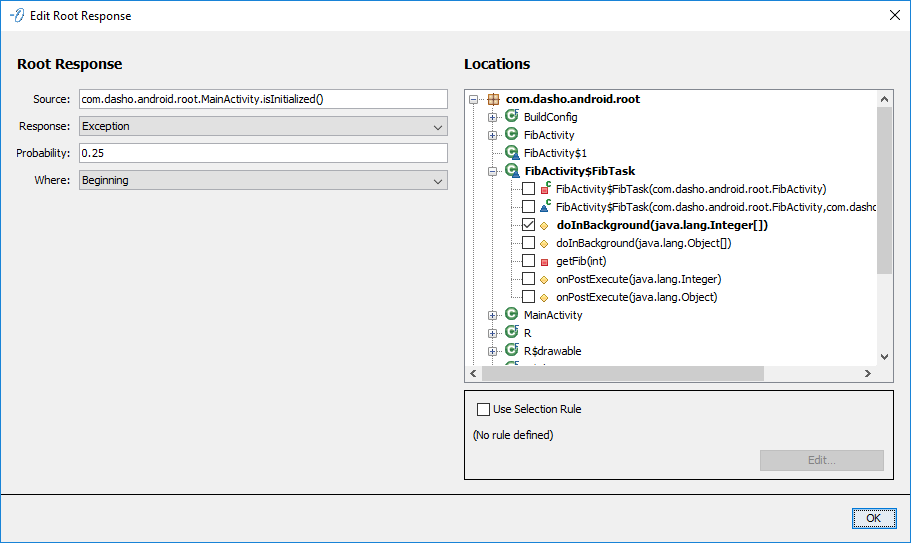
Configures a RootResponse to be injected in the selected Locations. The Root Response uses the standard configuration.
Checks — Shelf Life
The Checks — Shelf Life panel is where you configure ShelfLifeChecks in your application. DashO uses this information to create an expiration token that is placed inside your code to enforce the expiration policy. The Check is injected based on the locations configured on this screen or where a @ShelfLifeCheck code annotation is used.
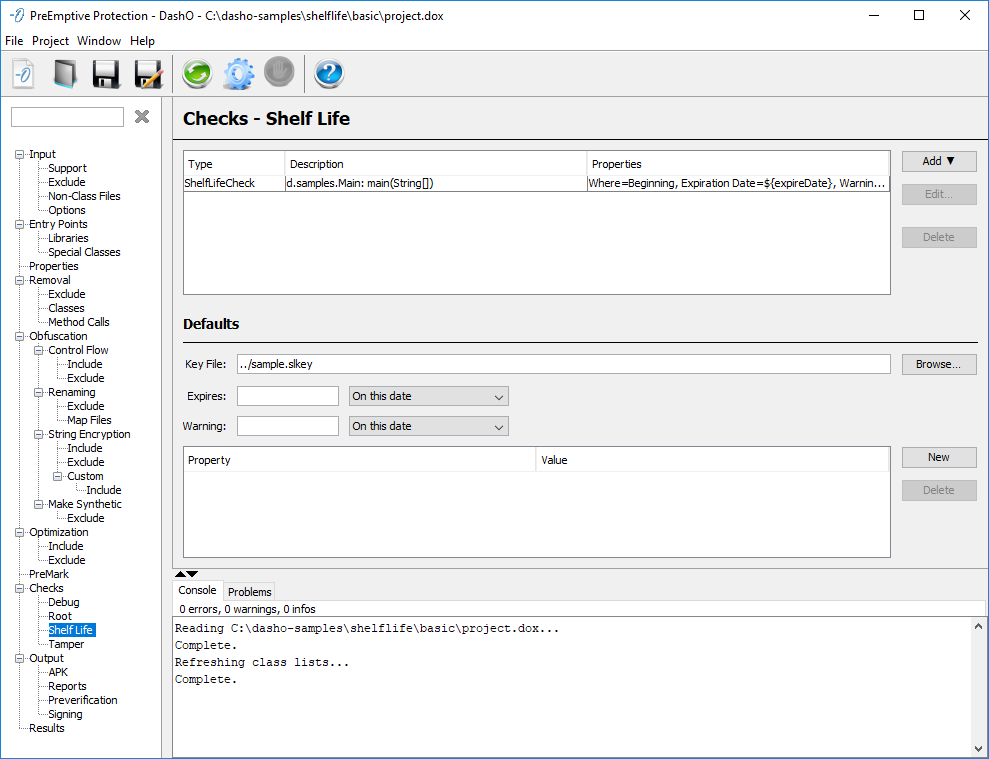
The Type column shows the type of Check. The Description column describes the locations in the code, the methods and classes, where the Checks will be injected. The Properties column shows the settings for that particular Check. The tooltips expand to show more details about the locations or properties.
Defaults
The information defined here is used for all individual Checks, unless the Check(s) overrides these defaults. It is also used to define properties to be added to the generated tokens.
Key File
Enter the location of the Shelf Life key file you received from PreEmptive Solutions. This file authorizes you to add Shelf Life Checks to your application.
Expiration Date
Your application can be configured to expire on an explicit date or a certain number of days after a dynamically determined start date. Dates are always in MM/DD/YYYY format regardless of the local convention.
Warning Date
Your application can be configured to issue expiration warnings starting on either an explicit date or a certain number of days before it is due to expire. Dates are always in MM/DD/YYYY format regardless of the local convention.
Properties
You can add arbitrary properties to the expiration token that can be retrieved by your application. To use this feature you need to supply a user defined action to the ShelfLifeCheck – this action method is passed the expiration token where you will be able to retrieve these properties. Note that both the property name and values can contain DashO property references.
Note:
The information supplied on this panel can be overridden or supplemented by aShelfLifeCheckor a@ShelfLifeCheckcode annotation.
Shelf Life Check
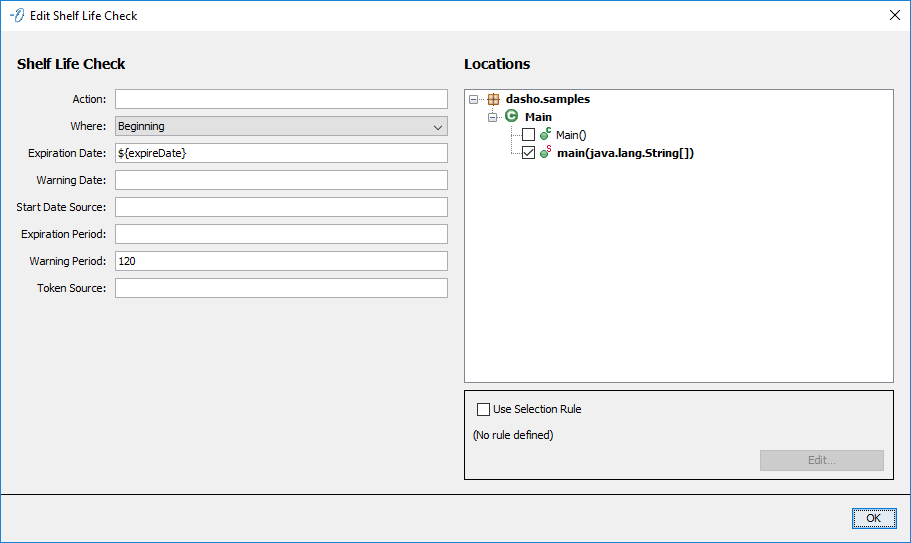
Configures a ShelfLifeCheck to be injected in the selected Locations. The Shelf Life Check has all the standard fields except Response and adds six additional fields:
- Expiration Date - Absolute date that the application expires in
MM/DD/YYYYformat. - Warning Date - Absolute date that warnings about expiration will start to be emitted in
MM/DD/YYYYformat. - Start Date Source - Source for the start date provided at runtime as a
java.util.Date. See Specifying Sources and Actions for more information. - Expiration Period - Relative expiration date in number of days since the start date.
- Warning Period - Relative warning date in number of days until the expiration date.
- Token Source - Source of the Shelf Life token as a
java.io.Readerif managing it externally. See Specifying Sources and Actions for more information.
Checks — Tamper
The Checks — Tamper panel is where you configure TamperChecks and TamperResponses.
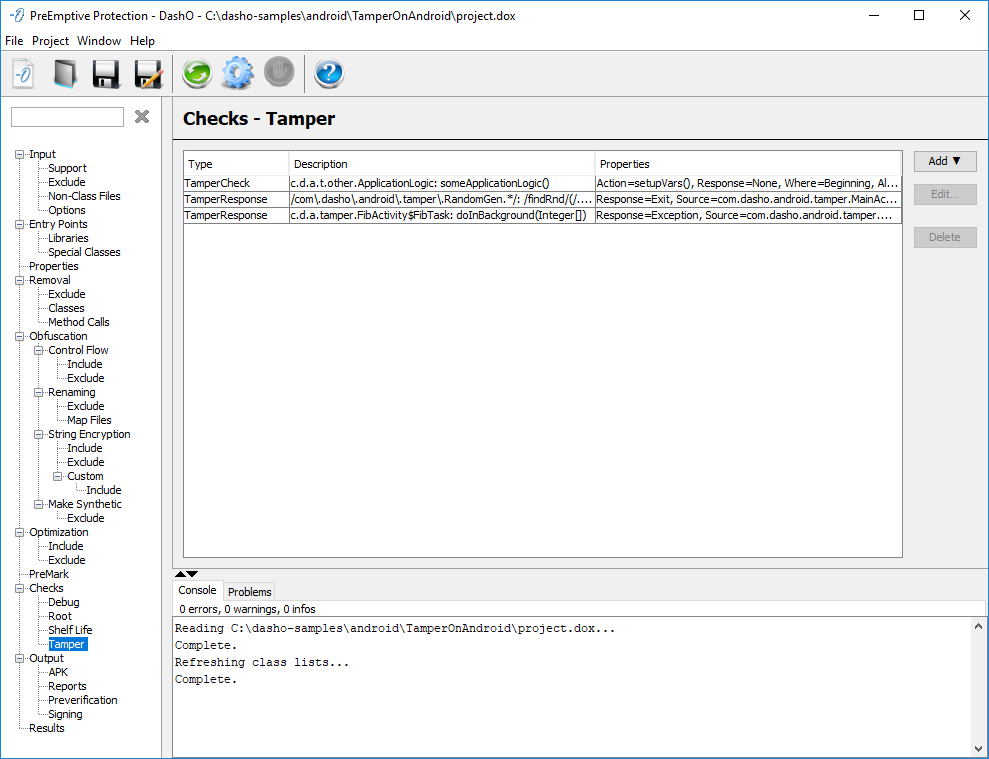
The Type column shows the type of Check or Response. The Description column describes the locations in the code, the methods and classes, where the Check or Response will be injected. The Properties column shows the settings for that particular Check or Response. The tooltips expand to show more details about the locations or properties.
Tamper Check
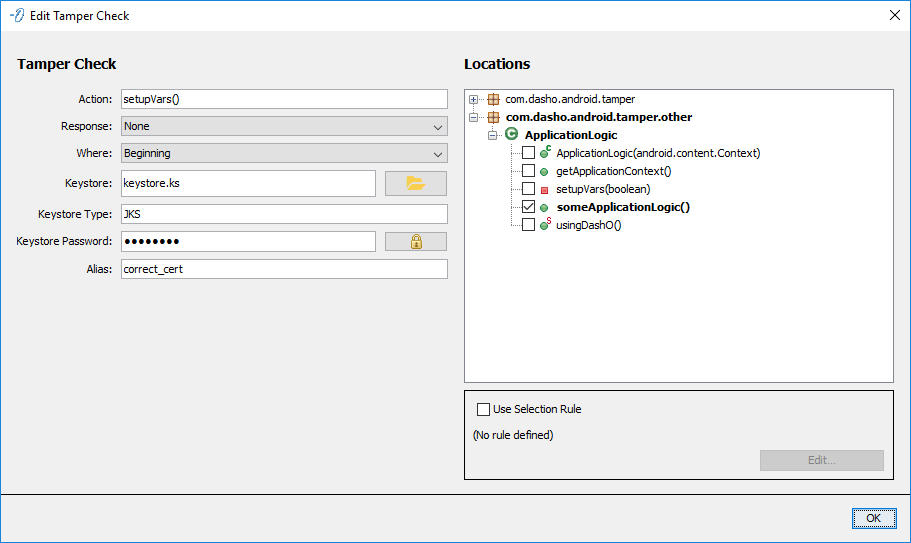
Configures a TamperCheck to be injected in the selected Locations. The Tamper Check has all the standard fields and adds four additional fields:
- Keystore - The URL to the key store; defaults to
.keystorein the user's home directory. May reference DashO properties. - Keystore Type - The type of the key store; defaults to the type specified by the JVM running DashO (e.g.
JKSorPKCS12). May reference DashO properties. - Keystore Password - The password for the key store. The user interface stores this in an encoded form but the value can be in plain text. May reference DashO properties.
- Alias - The alias used to store the private key in the key store. May reference DashO properties.
Note: If these four fields are left blank, the key store and alias information from the Output-Signing page will be used.
Tamper Response
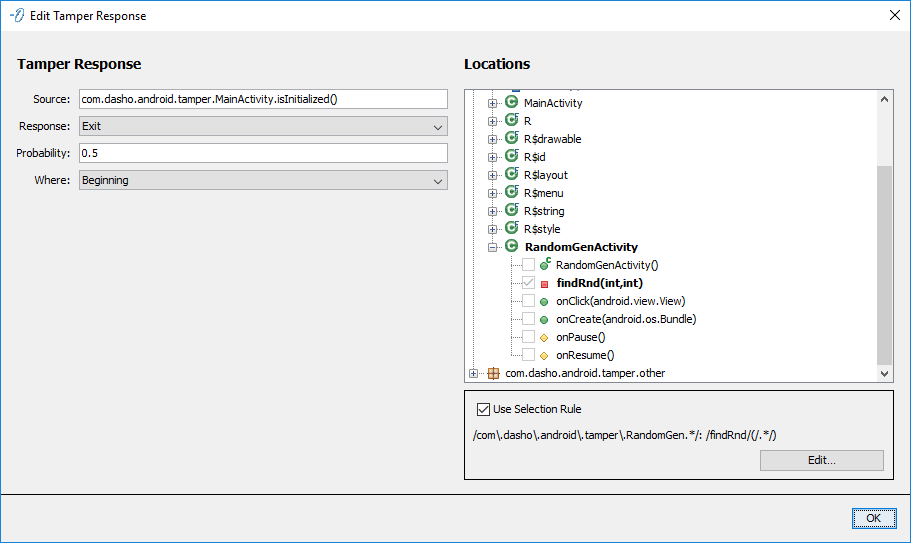
Configures a TamperResponse to be injected in the selected Locations. The Tamper Response uses the standard configuration.
Configuring Checks and Responses
Checks
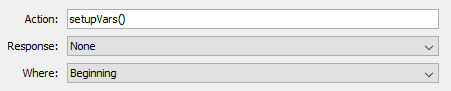
Checks have many common configuration elements:
- Action - An optional custom action. See Specifying Sources and Actions for more information. This
actionwill generally be passedtruewhen triggered andfalsewhen not. - Response - The response to take when the Check is triggered.
- None – Do nothing (default).
- Exit – Exit the application with a random, non-zero return code.
- Hang – Cause the current thread, which is running the injected Check, to hang indefinitely.
- Error – Throw a randomly selected subclass of
java.lang.Error. - Exception – Throw a randomly selected unchecked subclass of
java.lang.Exception.
- Where - Where in the method should the code be injected?
- Beginning – The beginning of the method (default).
- End – The end of the method.
- Beginning and End – Both the beginning and end of the method.
- Locations - Where should the Check be inserted? See Locations.
Responses
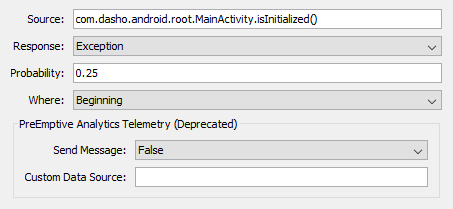
All Responses work in a similar fashion to each other:
- Source - The source to determine if the Check has been triggered. See Specifying Sources and Actions for more information.
- Response - The response to take when the
sourceindicates the Check was triggered (i.e.true).- None – Do nothing (default).
- Exit – Exit the application with a random, non-zero return code.
- Hang – Cause the current thread, which is running the injected Response, to hang indefinitely.
- Error – Throw a randomly selected subclass of
java.lang.Error. - Exception – Throw a randomly selected unchecked subclass of
java.lang.Exception.
- Probability - The probability the
Response(i.e.Exit,Hang,ErrororException) should happen. Expects a decimal from0.0to1.0(default:1.0). - Where - Where in the method should the code be injected?
- Beginning – The beginning of the method (default).
- End – The end of the method.
- Beginning and End – Both the beginning and end of the method.
- Locations - Where should the Response be inserted? See Locations.
Locations
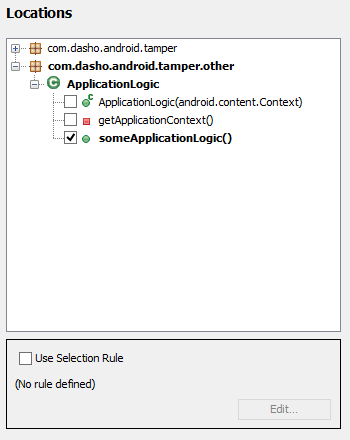
Checks and Responses can be injected into one or more places. You can select the methods manually or create a Selection Rule.
Selection Rule
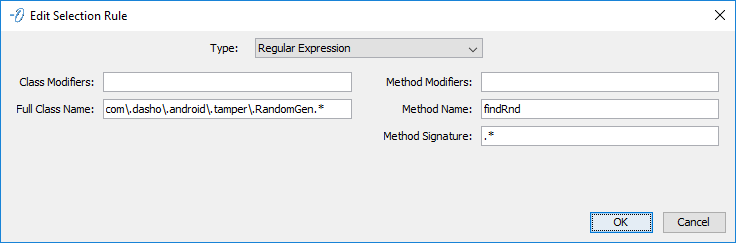
Configures a Pattern or Regular Expression to determine which method or methods to select.
- Type - Regular Expression or Pattern.
- Class Modifiers - The optional class modifiers.
- Full Class Name - The fully-qualified name of the class.
- Method Modifiers - The optional method modifiers.
- Method Name - The name of the method.
- Method Signature - The method signature.
Notes:
The name and signature fields must contain valid entries.
See the description of the Modifiers attribute for values to use for the optional modifiers.
See Patterns and Regular Expressions for values to use for the names and the signature.